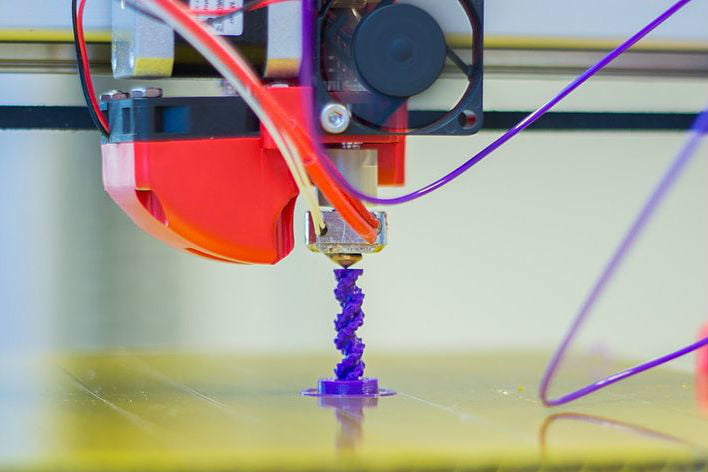
3D printing is a relatively new invention that allows users to design an
object and ahve it printed out right in front of them. It creates the
object from a design it is told to print and adds on layers to the base
until the object is finished being built. 3D printing has continued to evolve
over the past few years, but the basics of it are still mostly the same.
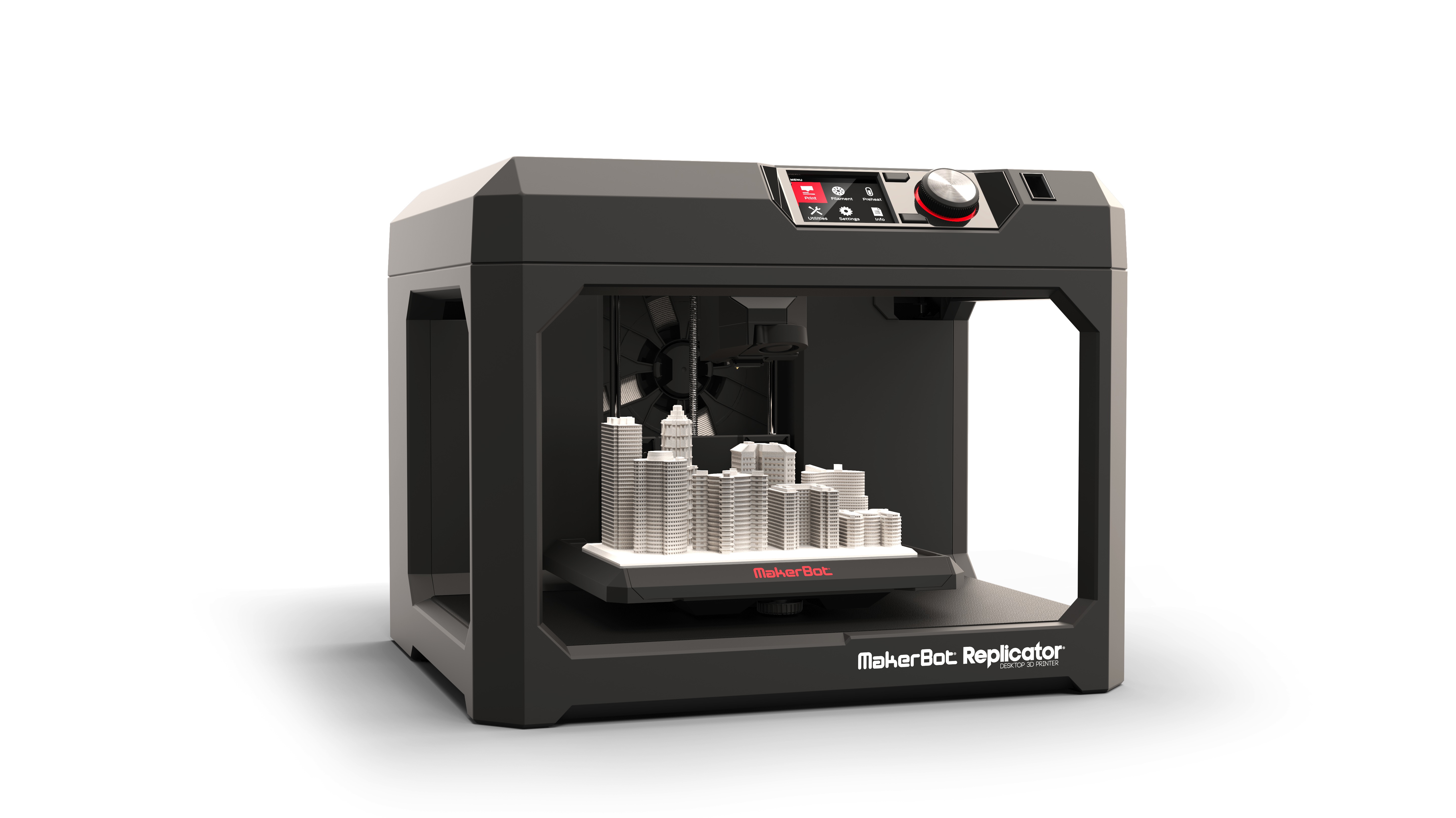

Digital File, Printing Machine and Material
The machine uses direction a digital file to create the 3d object.
Once the file is uploaded to the printer, it can print smoothly.
The file gives the printer an accurate layer-by-layer "instruction" on how
to print the object. Many 3D printers have different means by which they print the object, for example,
one might use a nozzle instead of a laser to lay down material, but one thing
they all have in common is their use of a sort of box where the material is laid down.
This space needs to be free of any obstruction to allow for the machine to successfully
print an object. Additionally, many printers will only operate in certain temperatures.
The material used when printing can vary as well. While it is usually colored plastic, some machines
use nylons, synthetic sandstone, metals such as steel or silver, and/or
resins to create a firmer base for the object. Certain machines can use multiple for a single
object.